Common problem
Do capacitors really cause the short life of LED lamps?
Source:本站 | Time:2021-11-18 | Read:792
Many people may have heard that the main reason for the short life of LED lamps is the short life of the power supply, and the main reason for the short life of the power supply is the electrolytic capacitors. Is this situation true? In fact, this statement is not completely without reason. Because there are many in the market today in order to fight the price, and ignore the quality of capacitors "disposable capacitors", these electrolytic capacitors low quality, short life, if not coincidentally LED lamp manufacturers with this capacitor, then the above short life of the phenomenon, is very likely to happen.
What is the real situation?
1、The ambient temperature of electrolytic capacitor will affect its life
We generally use "hour" to define the working life of electrolytic capacitors. Suppose the life time of an electrolytic capacitor is 1,000 hours, it doesn't mean that the capacitor will be scrapped after 1,000 hours, but the capacity of the capacitor will be reduced after 1,000 hours, if the capacitor is originally 20uF, it will be 10uF after the life time.
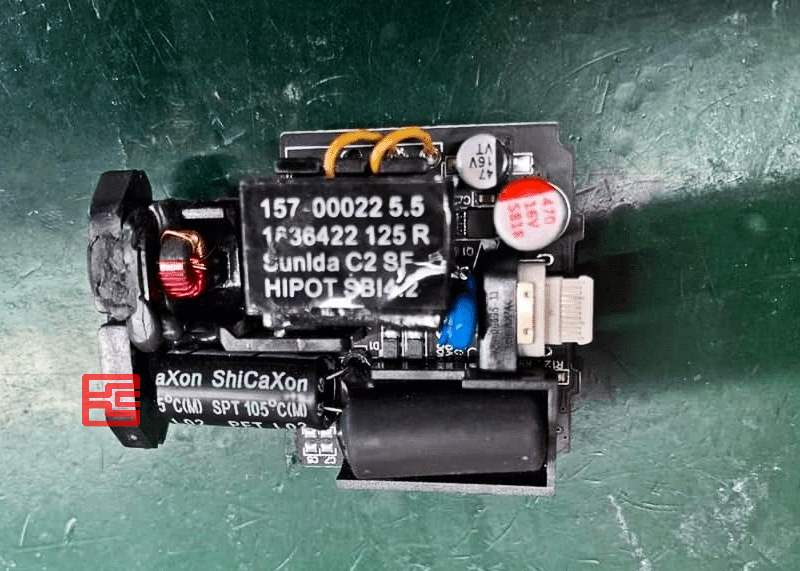
Besides, we should pay attention to one point when we use electrolytic capacitors, that is, we must state how many degrees the capacitor is allowed to be used in the working environment temperature, and cannot exceed the range. Generally capacitors are specified to have a life time at 105℃ ambient temperature.
Why is there such a rule? This is because we are now using liquid electrolyte electrolytic capacitors in the commonly used aluminum electrolytic capacitors, if the electrolyte dries up, the electric capacity is of course gone. Temperature will affect the electrolyte, and the higher the temperature of the working environment, the easier the electrolyte will evaporate. So the life index of electrolytic capacitors must indicate the life under what ambient temperature.
The most common electrolytic capacitors currently available are generally in the range of 105°C. An electrolytic capacitor, for example, has a life time of only 1,000 hours at 105°C. However, not all capacitors have only this life, and the SPT series is the most common series of capacitors produced by ShiCaXon, with black and white sleeves in color, and a capacitance life of 2,000H and an operating temperature of 105℃. PET sleeve is also available for special requirements of high temperature resistance.
For conventional capacitors in the market, simply speaking, if the ambient temperature is higher than 105℃, then its life time will be lower than 1,000 hours, and if the ambient temperature is lower than 105℃, then its life time will be higher than 1,000 hours. Thus, there is a rough quantitative relationship between the life of a capacitor and the temperature.
There is a simplest and easy to calculate relationship, that is, for every 10 degree increase in ambient temperature, the life time is reduced by half; conversely, for every 10 degree decrease in ambient temperature, the life time is doubled. Of course, this is only a simple estimate, but it is also more accurate.
Then the electrolytic capacitors used in LED driver power supply are definitely placed inside the LED lighting housing, so we just need to know the internal temperature of LED lighting to know the working life of electrolytic capacitors.
2、What is the ambient temperature in LED lamps and lanterns?
Simply speaking, the ambient temperature of LED and electrolytic capacitor is the same, because in many lamps and lanterns, both of them are placed in the same housing. The factors that affect the ambient temperature are mainly determined by the balance of heat and heat dissipation of LED and power supply. But because the heat and heat dissipation of each LED luminaire is not the same, so how can we know the ambient temperature inside it?
We can reverse the projection, that is, a well-designed LED luminaire, it allows the internal ambient temperature should be a certain. This is because the junction temperature of the LED chip is the main reason to determine the LED chip light failure (life), LED junction temperature is of course also related to its ambient temperature, so as long as we know the allowable LED junction temperature, we can also project the internal ambient temperature of the LED luminaire.
But there are at least three thermal resistance, that is, the LED chip junction to the shell of the thermal resistance θjc, and the LED shell to the surface of the aluminum substrate thermal resistance, which in fact after the solder, copper foil, and insulation layer and then to the aluminum plate, but the most important of which is the thermal resistance of the insulation layer, collectively referred to as θlv, the third is the thermal resistance of the aluminum plate to the air inside the bubble θla.
Take the 3014 LED, its own thermal resistance θjc is 90 ℃ / W, because its power is only 0.1W, so the temperature difference between inside and outside is 9 ℃. Aluminum substrate thermal resistance is 1 ℃ / W, for a 10W lamps and lanterns because all 10W LEDs are installed on the same aluminum substrate, so its total temperature difference is 10 ℃, a total of 19 ℃ temperature difference, the final θla is difficult to estimate, because it is related to whether the air flow, in the case of internal air does not flow, the temperature difference is probably only about 1 ℃, so it adds up to a total of 20 ℃ . In other words, the LED junction temperature is equal to the ambient temperature plus 20°C.
So the ambient temperature inside the bubble case can allow 105 degrees? Just take a look at one of the pictures below to find out. That is the relationship between the junction temperature and light decay of LED chips from Cree.
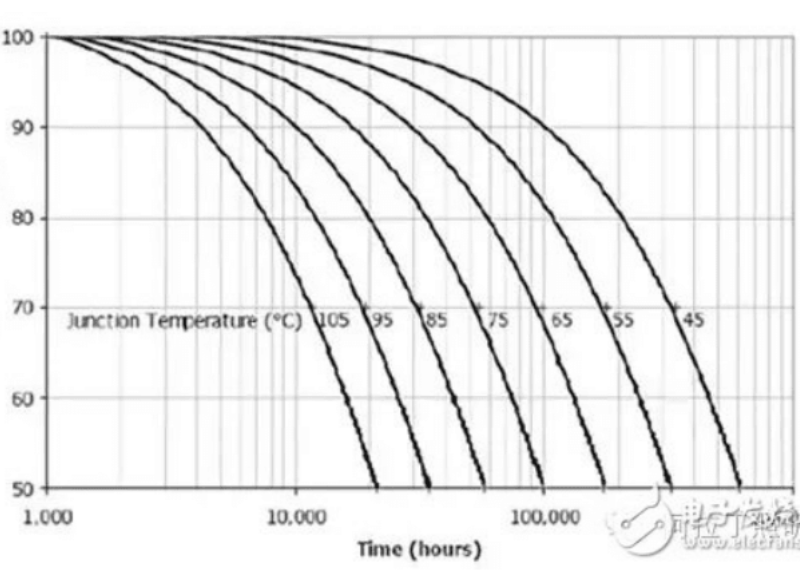
If the ambient temperature is 105 degrees Celsius, then also at least 20 degrees Celsius must be added to the junction temperature, so the junction temperature would be about 125 degrees Celsius. In this curve can no longer be found, can only roughly estimate the life of only 4,000 hours. This is absolutely unacceptable! In other words, the ambient temperature in the LED bubble must be much lower than 105 ℃!
What is the real situation?
1、The ambient temperature of electrolytic capacitor will affect its life
We generally use "hour" to define the working life of electrolytic capacitors. Suppose the life time of an electrolytic capacitor is 1,000 hours, it doesn't mean that the capacitor will be scrapped after 1,000 hours, but the capacity of the capacitor will be reduced after 1,000 hours, if the capacitor is originally 20uF, it will be 10uF after the life time.

Besides, we should pay attention to one point when we use electrolytic capacitors, that is, we must state how many degrees the capacitor is allowed to be used in the working environment temperature, and cannot exceed the range. Generally capacitors are specified to have a life time at 105℃ ambient temperature.
Why is there such a rule? This is because we are now using liquid electrolyte electrolytic capacitors in the commonly used aluminum electrolytic capacitors, if the electrolyte dries up, the electric capacity is of course gone. Temperature will affect the electrolyte, and the higher the temperature of the working environment, the easier the electrolyte will evaporate. So the life index of electrolytic capacitors must indicate the life under what ambient temperature.
The most common electrolytic capacitors currently available are generally in the range of 105°C. An electrolytic capacitor, for example, has a life time of only 1,000 hours at 105°C. However, not all capacitors have only this life, and the SPT series is the most common series of capacitors produced by ShiCaXon, with black and white sleeves in color, and a capacitance life of 2,000H and an operating temperature of 105℃. PET sleeve is also available for special requirements of high temperature resistance.
For conventional capacitors in the market, simply speaking, if the ambient temperature is higher than 105℃, then its life time will be lower than 1,000 hours, and if the ambient temperature is lower than 105℃, then its life time will be higher than 1,000 hours. Thus, there is a rough quantitative relationship between the life of a capacitor and the temperature.
There is a simplest and easy to calculate relationship, that is, for every 10 degree increase in ambient temperature, the life time is reduced by half; conversely, for every 10 degree decrease in ambient temperature, the life time is doubled. Of course, this is only a simple estimate, but it is also more accurate.
Then the electrolytic capacitors used in LED driver power supply are definitely placed inside the LED lighting housing, so we just need to know the internal temperature of LED lighting to know the working life of electrolytic capacitors.
2、What is the ambient temperature in LED lamps and lanterns?
Simply speaking, the ambient temperature of LED and electrolytic capacitor is the same, because in many lamps and lanterns, both of them are placed in the same housing. The factors that affect the ambient temperature are mainly determined by the balance of heat and heat dissipation of LED and power supply. But because the heat and heat dissipation of each LED luminaire is not the same, so how can we know the ambient temperature inside it?
We can reverse the projection, that is, a well-designed LED luminaire, it allows the internal ambient temperature should be a certain. This is because the junction temperature of the LED chip is the main reason to determine the LED chip light failure (life), LED junction temperature is of course also related to its ambient temperature, so as long as we know the allowable LED junction temperature, we can also project the internal ambient temperature of the LED luminaire.
But there are at least three thermal resistance, that is, the LED chip junction to the shell of the thermal resistance θjc, and the LED shell to the surface of the aluminum substrate thermal resistance, which in fact after the solder, copper foil, and insulation layer and then to the aluminum plate, but the most important of which is the thermal resistance of the insulation layer, collectively referred to as θlv, the third is the thermal resistance of the aluminum plate to the air inside the bubble θla.
Take the 3014 LED, its own thermal resistance θjc is 90 ℃ / W, because its power is only 0.1W, so the temperature difference between inside and outside is 9 ℃. Aluminum substrate thermal resistance is 1 ℃ / W, for a 10W lamps and lanterns because all 10W LEDs are installed on the same aluminum substrate, so its total temperature difference is 10 ℃, a total of 19 ℃ temperature difference, the final θla is difficult to estimate, because it is related to whether the air flow, in the case of internal air does not flow, the temperature difference is probably only about 1 ℃, so it adds up to a total of 20 ℃ . In other words, the LED junction temperature is equal to the ambient temperature plus 20°C.
So the ambient temperature inside the bubble case can allow 105 degrees? Just take a look at one of the pictures below to find out. That is the relationship between the junction temperature and light decay of LED chips from Cree.

If the ambient temperature is 105 degrees Celsius, then also at least 20 degrees Celsius must be added to the junction temperature, so the junction temperature would be about 125 degrees Celsius. In this curve can no longer be found, can only roughly estimate the life of only 4,000 hours. This is absolutely unacceptable! In other words, the ambient temperature in the LED bubble must be much lower than 105 ℃!



